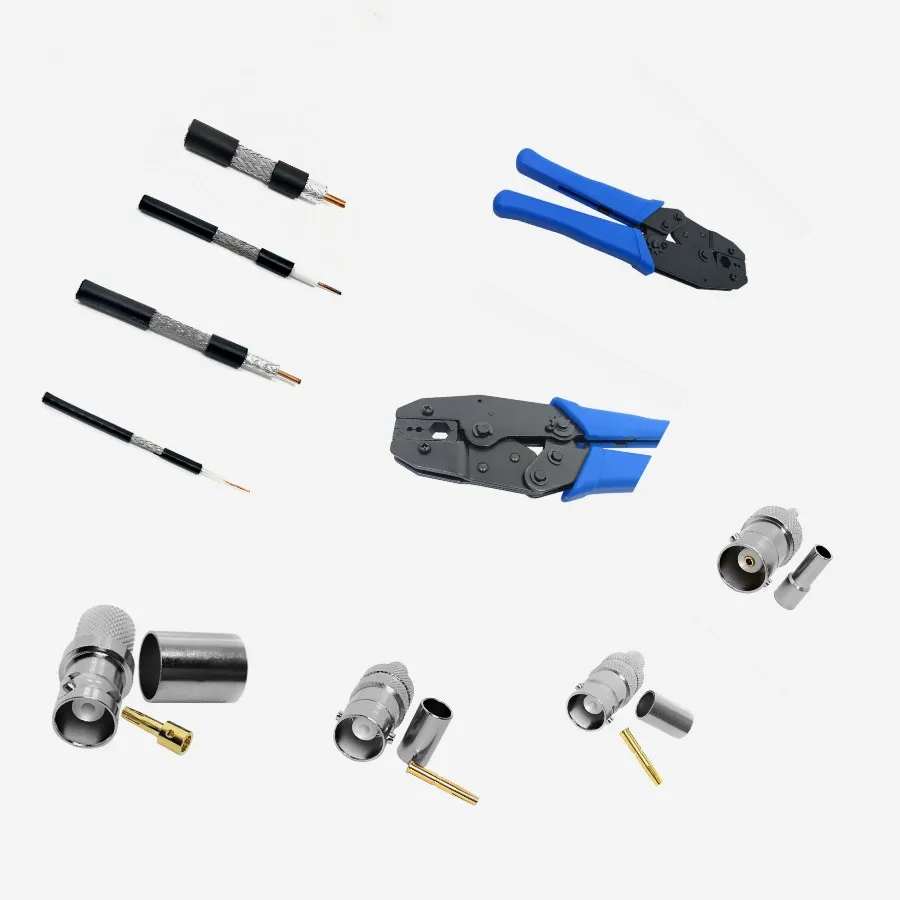
BNC Connector
- Brief introduction
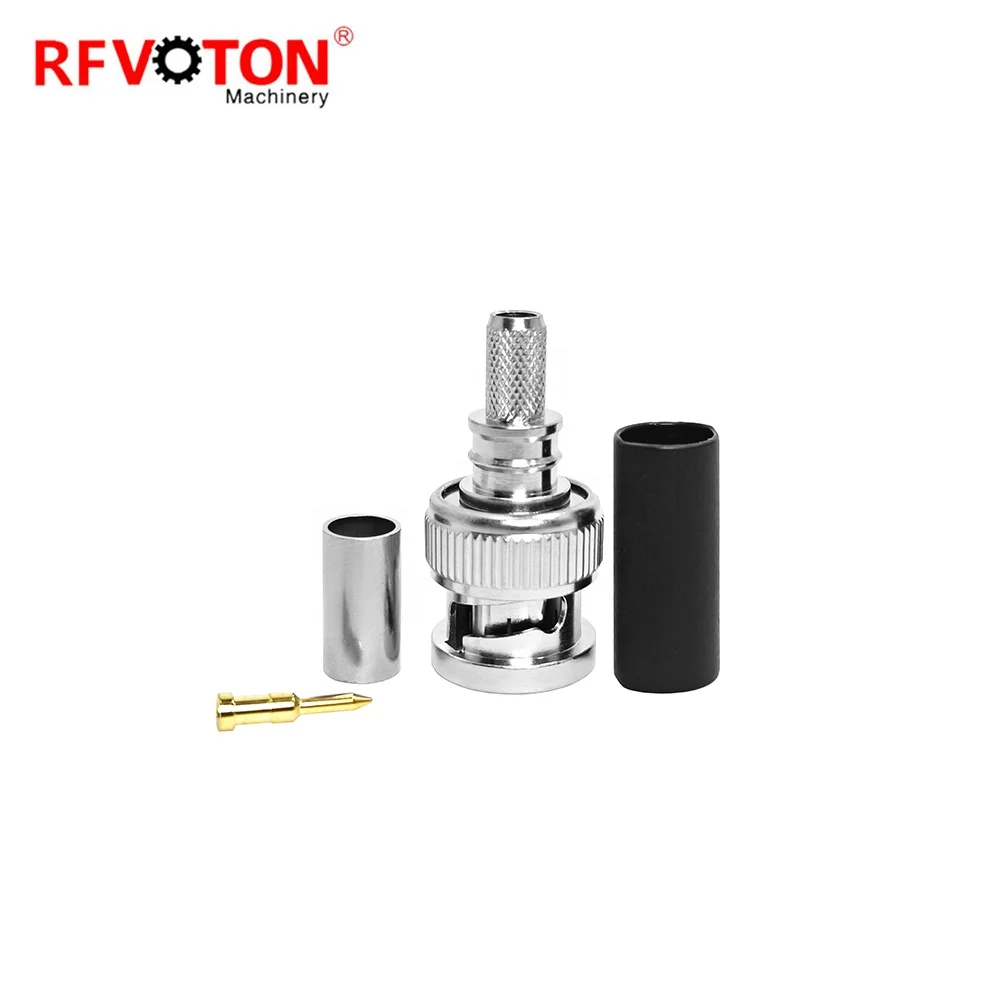
BNC connector (English: Bayonet Neill Concelman, literally translated as "Neill Concelman bayonet") is a very common RF terminal coaxial cable terminator. The BNC cable connector consists of a center pin, a jacket, and a socket. It includes three parts: BNC connector base, outer cover, and probe. The BNC connector is named after its locking mechanism and its inventors, Paul Neill of Bell Labs (who invented the N terminal) and Karl Conceman of Amphenol (who invented the C terminal). BNC cable connectors must be connected to both ends of each cable segment.

- Type
BNC connectors include:
1. BNC-T head, used to connect computer network cards and cables in the network;
2. BNC barrel connector, used to connect two thin cables into a longer cable;
3. BNC cable connector, used for welding or twisting at the end of the cable;
4. BNC terminator, used to prevent interference caused by signal reflection back after reaching the cable break. A terminator is a special type of connector that contains a carefully selected resistor that matches the characteristics of the network cable. Each terminal must be grounded.

- Quality assessment
1.From the surface of the product, it is better to have a bright and delicate coating. The higher the purity of copper, the brighter it is. Some products have a bright exterior but are made of iron.
2. For the adsorption test of magnetite, generally only the bayonet spring and tail spring are made of iron materials; The wire clamp, pins, and casing are made of copper, while other components are made of zinc alloy.
3. Scratch off the surface coating to see the material: Use sharp tools such as blades to scrape off the surface coating to visually see the material, and compare the product material by scraping off the coating of wire clamps, pins, and shielding sleeves.
In addition to the above methods, you can also prepare a high-quality female head for testing.

- Origin
BNC connectors are very similar to B and C terminals. A threaded connector TNC (Threaded Neill Concelman) has better performance in the microwave band compared to BNC.

- Specifications
BNC connectors come in two versions: 50 ohm and 75 ohm.
When connecting a 50 ohm connector to other impedance cables, the likelihood of transmission errors is relatively low. Different versions of connectors are compatible with each other, but if the cable impedance is different, the signal may be reflected. Usually, BNC connectors can be used at 4GHz or 2GHz.
The 75 ohm connector is used for connecting video and DS3 to the central office of the telephone company, while the 50 ohm connector is used for data and RF transmission. Incorrect connection of a 50 ohm plug to a 75 ohm socket may damage the socket. Use 75 ohm connectors in very high frequency applications.

- Instructions
BNC connectors are used for the transmission of RF signals, including the transmission of analog or digital video signals, the connection of amateur radio equipment antennas, the connection of aviation electronic equipment, and other electronic testing equipment. In the field of consumer electronics, BNC connectors used for video signal transmission have been replaced by RCA terminals. With a simple adapter, RCA terminals can be used on devices that only have BNC connectors.
BNC terminals were widely used in 10base2 Ethernet, but due to the replacement of coaxial cables with twisted pair cables, it is difficult to see network cards with BNC terminals. Some ARCNET networks terminate coaxial cables with BNC terminals.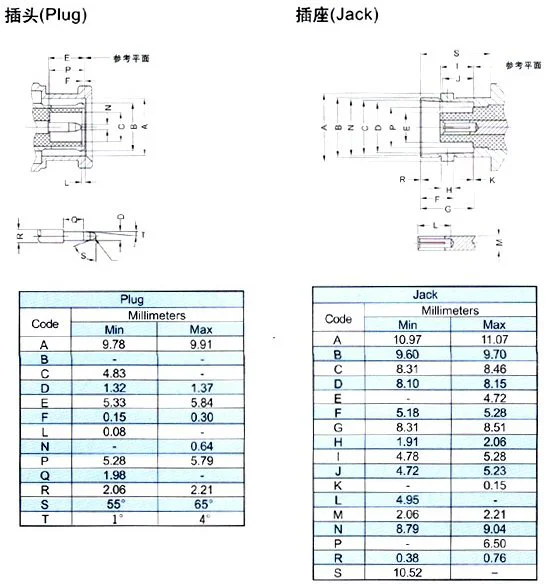
- Similar connectors
BNC connectors are commonly used in NIM, but have been replaced by the smaller LEMO 00. Under high voltage conditions, MHV connectors and SHV connectors are more common. MHV connectors can be forcibly connected to BNC connectors. SHV is a safer connector developed as a result, and it cannot be connected to regular BNC connectors.
In the former Soviet Union region, BNC connectors were replicated as SR-50 (Russian: Tsar-50) and SR-75 (Tsar-75) connectors. Due to the conversion from imperial to metric, these connectors are different from BNC but can be forcibly connected. The dual plug BNC (also known as dual axis BNC) connection uses the same knife lock housing as BNC, but includes two independent contact points (a pair of plug sockets), allowing for the connection of 78 ohm or 95 ohm differential pairs, such as RG-108A.
They can operate at 100GHz and 100V. The dual BNC connector is not compatible with regular BNC connectors. Three axis BNC (also known as TRB) simultaneously connects signals, shielding layers, and grounding. Used in sensitive electronic measurement systems, it cannot be directly used with BNC connectors, but can be connected to general BNC connectors through adapters.
Hot News
-
What is RF coaxial connector? What are the characteristics and applications?
2025-07-01
-
BNC Connector
2024-07-22
-
SMA connector
2024-07-19
-
The difference between BNC connectors and SMA connectors
2024-07-03
-
What are the advantages of anti-interference coaxial cables
2023-12-18
-
Complete Guide to Basic Knowledge of Coaxial Connectors
2023-12-18
-
Why is the anti-interference ability of coaxial cables so strong
2023-12-18

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 UR
UR
 HA
HA
 JW
JW
 LA
LA
 MY
MY
 KK
KK
 TG
TG
 UZ
UZ
 AM
AM
 PS
PS

